NTP Server
Here are some useful commands when running a GPS-disciplined NTP server.
See this page for the local NTP server (192.168.1.12): Local GPS NTP Time Server
NTPQ
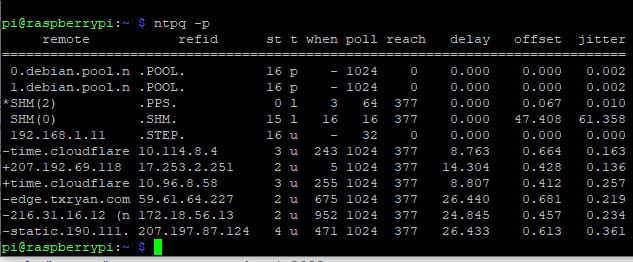
When running a query of an ntp server, you would use: ntpq -p.
What you see is this:
ntpq -pn
Here’s an explanation:
REMOTE = The servers and peers specified in the configuration file, from which your host will take time synchronization
Character that may prefix the remote hostname/IP address:
-
indicates the current synchronization source.
# indicates that the host is selected for synchronization, but distance from the host to the server exceeds the maximum value.
o indicates that the host is selected for synchronization and the PPS signal is in use.
+ indicates the host is included in the final synchronization selection set.
x indicates that the host is the designated false ticker by the intersection algorithm.
. indicates that the host is selected from the end of the candidate list.
– indicates a host discarded by the clustering algorithm.
blank indicates a host is discarded due to high stratum and/or failed sanity checks.
REFID = the current source of synchronization for the remote host
ST = the stratum level of the remote host
T = types available:
l local (such as a GPS clock)
u unicast (this is the common type)
m multicast
b broadcast
– netaddr (usually 0)
WHEN = number of seconds passed since the remote host response
POLL = polling interval to the remote host, defined with the “minpoll” value in ntp.conf file
REACH = indicates how successful attempts to reach the server are. This is an 8-bit shift register with the most recent probe in the 2^0 position. The value 001 indicates the most recent probe was answered, while 357 indicates one probe was not answered. The value 377 indicates that all the recent probes have been answered.
DELAY = (round trip time) indicates the time (in milliseconds) taken by the reply packet to return in response, to a query sent by the server.
OFFSET = indicates the time difference (in milliseconds) between the server’s clock and the client’s clock. When this number exceeds 128, and the message synchronization lost appears in the log file
JITTER = indicates the difference in the offset measurement between two samples. This is an error-bound estimate. Jitter is a primary measure of the network service quality.
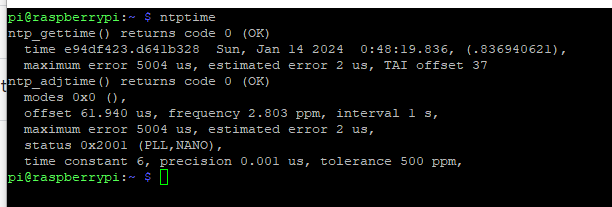
NTPTIME
This command will give you the current time as:
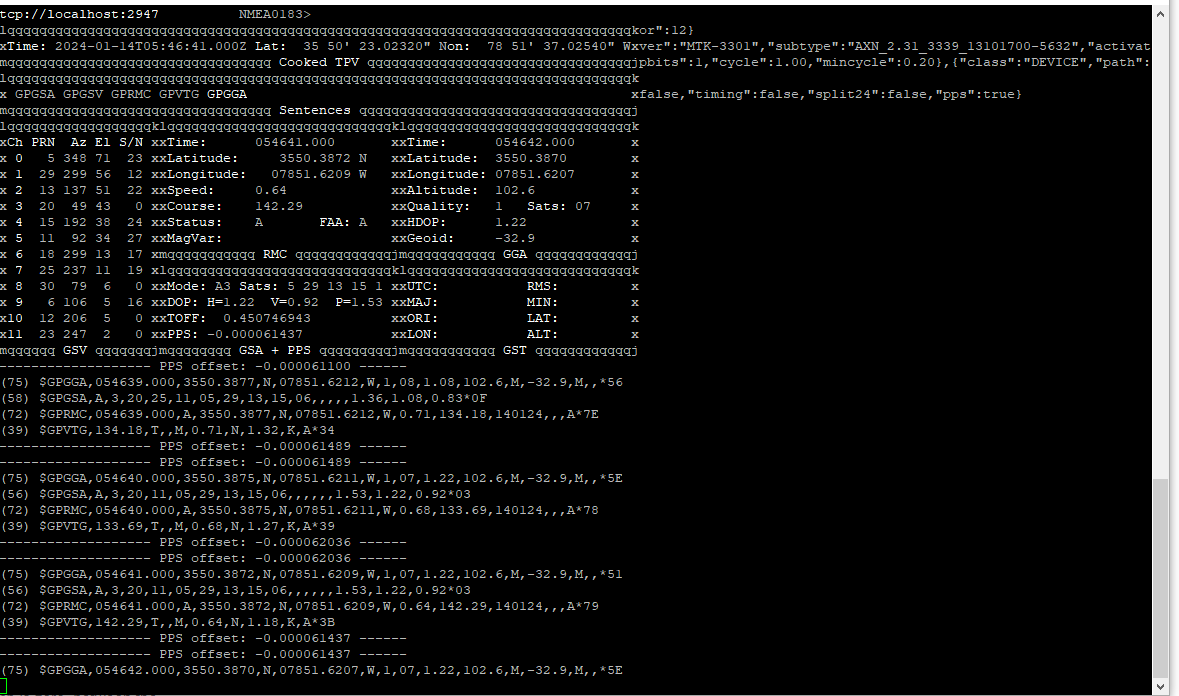
GPSMON
This is used to get access to a semi-graphical display of raw GPS location and time data.
The output looks like this:

No Comments